Information about the Schengen Visa
With the Schengen Visa you are able to travel without border checks The Schengen visa entitles you to travel and stay in the Schengen area. Here we will provide you with important information about the visa with easily understandable explanations
Home Schengen Visa
Topics at a glance
The Schengen visa explained in brief
The Schengen visa is valid in 27 countries that have signed a joint travel agreement. Of those countries, 23 Schengen are part of the EU. In addition, Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland have joined the Schengen Agreement. Only the three European countries Great Britain, Ireland and Cyprus are not part of the agreement.
The Schengen Agreement prescribes a uniform visa regulation for member states. In principle, the Schengen visa allows free travel (without border checks) in the Schengen area for a maximum of 90 days in a 6-month period.
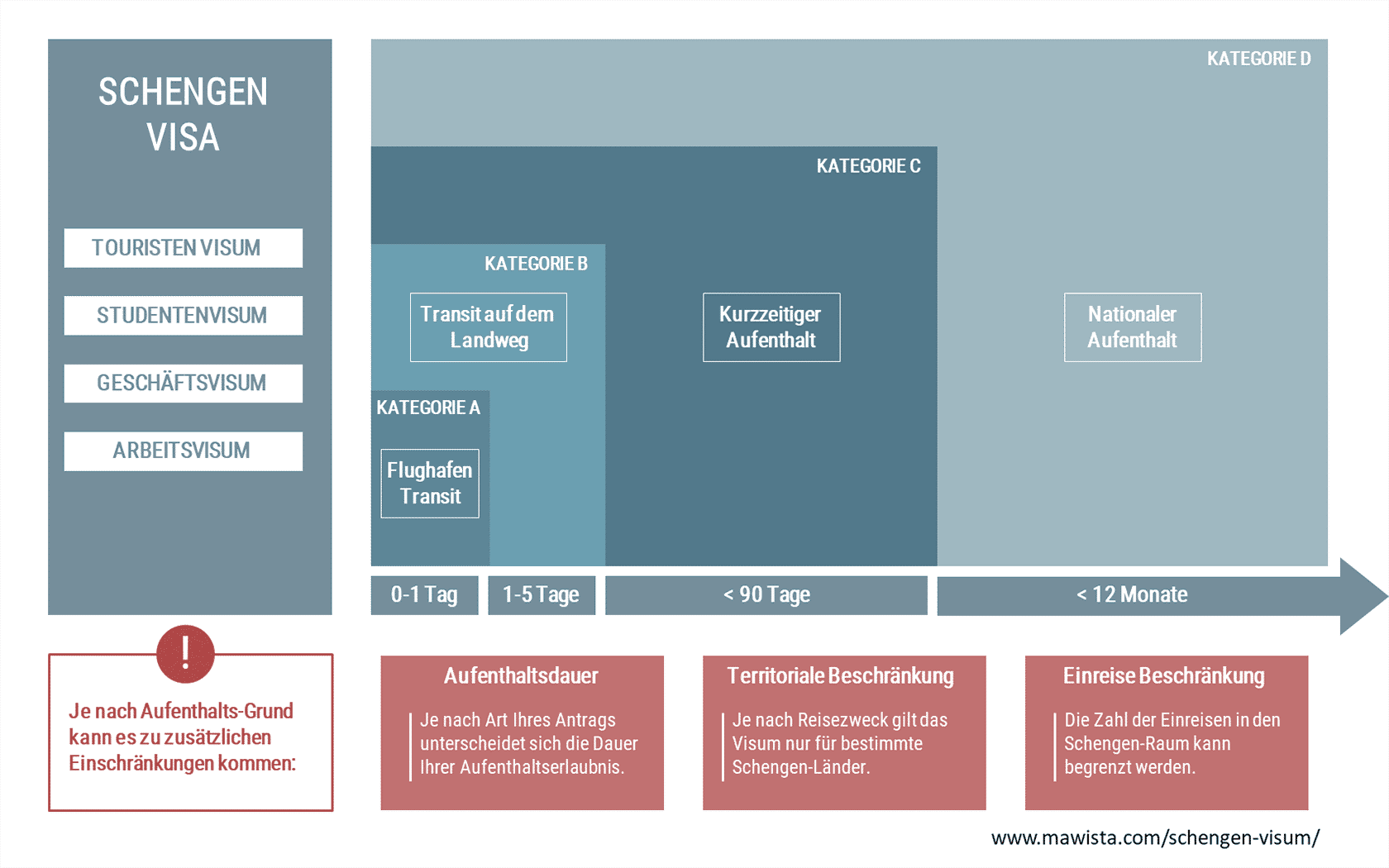
There are different types of residence permits, called categories. The category (A, C, D) you should apply for depends on the purpose of your trip (for example, private, for educational or professional purposes) and the length of your stay. under the new Visa Code, category B is also covered by the general Schengen visa (category C).
Depending on your specific situation, special visas (such as work permits) and restrictions (such as area restrictions, restrictions on entry frequency) are recorded in the visa.
You can apply for a visa in your home country at the embassy or consulate of the country where you will spend most of your time. It is important to submit all required documents in full, otherwise your application cannot be approved. The fee will be paid directly to the responsible embassy upon application.
The following graph shows the relationship between visa categories (A, C, D) and length of stay. The different types of visas and possible restrictions are also part of the overview. Further information can be found in this text linked or in the topic choice.